Pixie-16 C API Example#
example_pixie16api compiles and links against Pixie16Api.so.
This library provides users a C wrapper to the PixieSDK. We also
provide a python example that uses the same configuration file and
library.
Prerequisites#
You have followed the PixieSDK installation instructions.
The Path variable has been updated with the full path to the example_pixie16api
Configuration file#
File Format#
The configuration file uses JSON. This file format is ideal as it provides us a semi-structured format that allows expansion without impacting older versions.
Slot Definition Order#
The software will automatically determine the number of requested modules in the system according to the number of objects in the array. Note that this is separate from the process that the SDK uses to identify the PLX 9054 devices present. The order of the objects defines the slot to module number mapping. For example, Slot 2 will map to Module 0.
Module definitions#
Each requested module must have a JSON array element. These elements contain the information necessary for the SDK to fully initialize and boot the hardware.
If using the firmware automatically loaded by the SDK, the base level configuration file needs only a slot number and a dsp par file for each module. Note that here custom firmware is defined as the user wanting to use firmware other than what is automatically loaded by the SDK.
Name |
Description |
Elements |
Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
slot |
Defines the physical slot this module occupies |
N/A |
Yes |
dsp |
Defines the settings file to load to the hardware |
par |
Yes |
fw |
Defines the firmware for this module |
adc_bits, adc_msps, fw_set, revision |
No |
fifo_config |
Used to setup the module’s list-mode worker FIFO configuration |
bandwidth_mb_per_sec, buffers, dma_trigger_level_bytes, hold_usecs, idle_wait_usecs, run_wait_usecs |
No |
See FIFO Configuration
for definitions and valid values of fifo_config elements.
Firmware Node#
A description of the firmware nodes. These values get used by PixieRegisterFirmware() to register a firmware set
with the module.
Name |
Description |
Type |
Example(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
adc_bits |
The bit resolution of the ADC |
integer |
12, 14, 16 |
adc_msps |
The sampling frequency of the ADC |
integer |
125, 250, 500 |
fw_set |
An object node that contains one or more of the following keys: dsp, fippi, sys, and var. The key’s value is a string that contains the absolute path to the device’s firmware. If the user provides a partial key list, then the default firmware will be overridden with the partial set. |
object |
“dsp”: <absolute or relative path to DSP LDR file> |
revision |
The revision of the module |
integer |
13, 15, 17 |
See Firmware Management and the glossary for information on the updated firmware architecture.
Config Examples#
The same configuration file is used on both Linux and Windows systems.
Please note that on Windows that \ characters in paths need to be
escaped. For example
"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\XIA\\Pixie16_VB 2.3.1\\DSP\\Pixie16DSP_revfgeneral_16b250m_r35921.ldr"
Templates#
The following three templates demonstrate how to use firmware infrastructure to use the automatic firmware finding, define a custom firmware (legacy operation), and define a partial firmware set.
Use system firmware#
[
{
"slot": "<slot number>",
"dsp": {
"par": "<absolute or relative path to JSON settings file>"
}
}
]
Define a custom firmware#
[
{
"slot": "<slot number>",
"dsp": {
"par": "<absolute or relative path to JSON settings file>"
},
"fw": {
"adc_bits": "<firmware ADC bit resolution>",
"adc_msps": "<firmware ADC frequency>",
"fw_set": {
"dsp": "<absolute or relative path to DSP LDR file>",
"fippi": "<absolute or relative path to FPGA FIPPI settings file>",
"sys": "<absolute or relative path to FPGA SYS settings file>",
"var": "<absolute or relative path to DSP VAR file>"
},
"revision": "<module revision>"
}
}
]
Override Default Firmware#
A partial firmware set uses one or more of the keys in the custom firmware to override just the file specified in the default system firmware.
[
{
"slot": "<slot number>",
"dsp": {
"par": "<absolute or relative path to JSON settings file>"
},
"fw": {
"adc_bits": "<firmware ADC bit rate>",
"adc_msps": "<firmware ADC frequency>",
"fw_set": {
"fippi": "<absolute or relative path to FPGA FIPPI settings file>"
},
"revision": "<module revision>"
}
}
]
Use-cases#
Single module configuration#
Defines a custom firmware set for the module in Slot 2.
[
{
"slot": 2,
"dsp": {
"par": "pixie.json"
},
"fw": {
"adc_bits": 16,
"adc_msps": 250,
"fw_set": {
"dsp": "/usr/local/xia/pixie/firmware/revf_general_16b250m_r35921/dsp.ldr",
"fippi": "/usr/local/xia/pixie/firmware/revf_general_16b250m_r35921/fippi.bin",
"sys": "/usr/local/xia/pixie/firmware/revf_general_16b250m_r35921/sys.bin",
"var": "/usr/local/xia/pixie/firmware/revf_general_16b250m_r35921/dsp.var"
},
"revision": 15
}
}
]
Single module configuration w/ FIFO config#
Use the default firmware for the module in Slot 2, but update its fifo configuration.
[
{
"slot": 2,
"dsp": {
"par": "pixie.json",
},
"fifo_config": {
"bandwidth_mb_per_sec": 0,
"buffers": 100,
"dma_trigger_level_bytes": 512,
"hold_usecs": 10000,
"idle_wait_usecs": 150000,
"run_wait_usecs": 5000
}
}
]
Settings Files#
Legacy binary settings files are not supported when using the parallel boot functionality. As the example software has moved away from serial booting, it is required that legacy settings files are not used when configuring the crate with the example software. Instead, use PixieSDK JSON settings files.
Generate an Empty Settings file#
In the case you do not have a settings file, an empty settings file can suffice. An empty settings file simply contains an empty JSON array. The Pixie SDK will automatically generate an appropriate settings file based on your system
[]
Execution#
These instructions assume that you’ve built and installed PixieSDK into the default location.
Linux#
Create the directory
mkdir ~/pixie_sdk_example && cd ~/pixie_sdk_example
Copy the sample configuration file from the repo
cp /usr/local/xia/PixieSDK/share/config/example_config.json .
Update the configuration file. You can name it whatever you want.
Execute the program to boot the modules
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/xia/PixieSDK/lib/ /usr/local/xia/PixieSDK/bin/example_pixie16api boot -c <name of config file>
Windows#
Windows will work similarly to Linux. You’ll need to add the PixieSDK library
and bin paths to your Path variable.
Usage#
usage: ./example_pixie16api <command name> <arguments>
commands
boot Boots the crate of modules.
copy Copies DSP parameters from source to
destination.
export-settings Boots the system and dumps the
settings to the file defined in the
config.
mca-export Exports histograms from the module
without executing a run.
init Initializes the SDK and prints module
information.
list-mode Starts a list mode data run
read Read a parameter from the module.
write Write a parameter to the module.
trace Captures ADC traces from the modules.
adjust_offsets Adjusts the DC offsets for all modules
in the config file.
baseline Acquire and print baselines from the
module
mca Starts an MCA data run.
blcut Starts a control task to find the
BLCut for a channel.
dacs Starts a control task to set the
module's DACs
tau_finder Executes the Tau Finder control task
and returns the values.
arguments
-c[cfg], --config=[cfg] The configuration file to read or
write. REQUIRED.
--additional-config=[cfg] The configuration file to load.
-h, --help Displays this message
-o[Offline Mode],
--offline=[Offline Mode] Tells the API to use Offline mode when
running.
-b[boot_pattern],
--boot_pattern=[boot_pattern] The boot pattern used for booting.
-n[parameter], --name=[parameter] The parameter we want to read from the
system.
-v[value], --value=[value] The value of the parameter we want to write.
--chan=[channel] The channel to operate on. If set to
the maximum number of channels in the
module, then reads/writes execute for
all channels.
--crate=[crate] The crate
--copy-mask=[copy_mask] An integer representing the set of parameters
to copy.
--dest-channel=[dest_channel] The channel that we'll copy to.
--dest-module=[dest_module] The module that we'll copt to.
--output-dir=[directory] The directory to write files to
-f[firmware_path],
--firmware=[firmware_path] The path to retrieve firmware from
--mod=[module] The module to operate on.
--num-runs=[num_runs] The number of runs to execute when
taking list-mode or MCA data.
-t[run_time], --time=[run_time] The amount of time that a data run will take
in seconds.
--synch-wait=[synch_wait] SynchWait = 0 to start/stop runs independently (default)
SynchWait = 1 to start/stop runs synchronously
--in-synch=[in_synch] InSynch = 0 to reset clocks prior to starting a run (default)
InSynch = 1 to take no clock action
Example commands#
Boot#
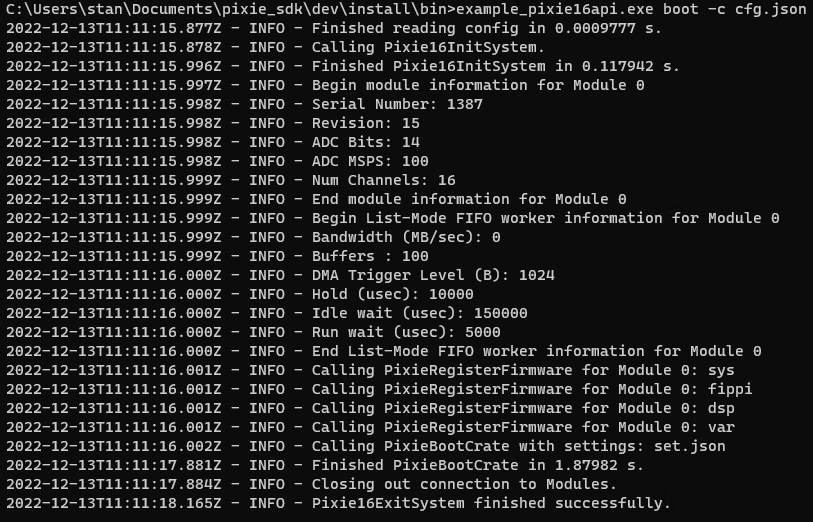
example_pixie16api boot -c cfg.json
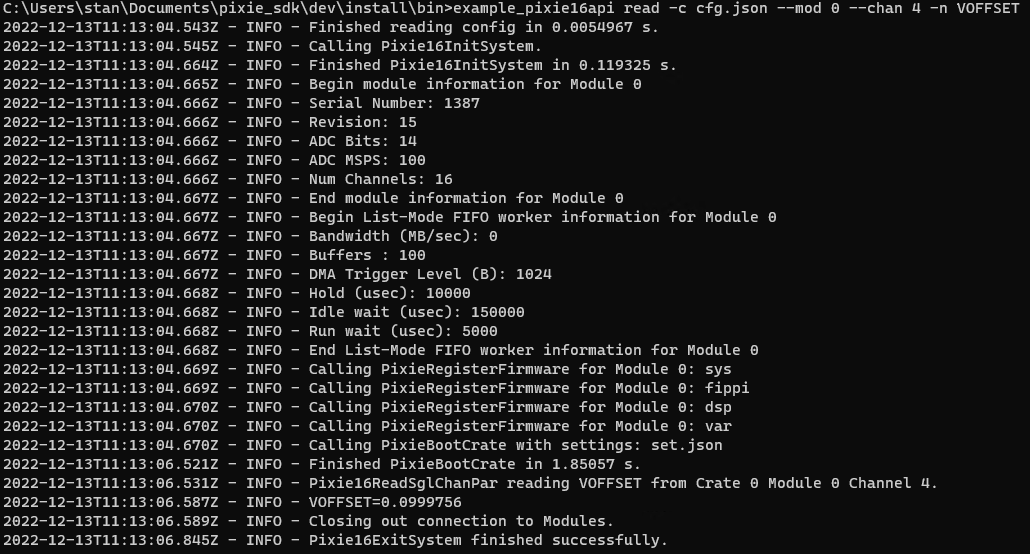
Read from a Channel#
example_pixie16api read -c cfg.json --mod 0 --chan 4 -n VOFFSET
Read from all Channels in a Module#
Note
Providing a channel number greater than the number of channels in the system will execute against all channels.
example_pixie16api read -c cfg.json --mod 0 --chan 16 -n VOFFSET
Read from a Module#
example_pixie16api read -c cfg.json --mod=0 -n HOST_RT_PRESET
Write to a Channel#
example_pixie16api write -c cfg.json --mod 0 --chan 6 -n VOFFSET -v 0.37
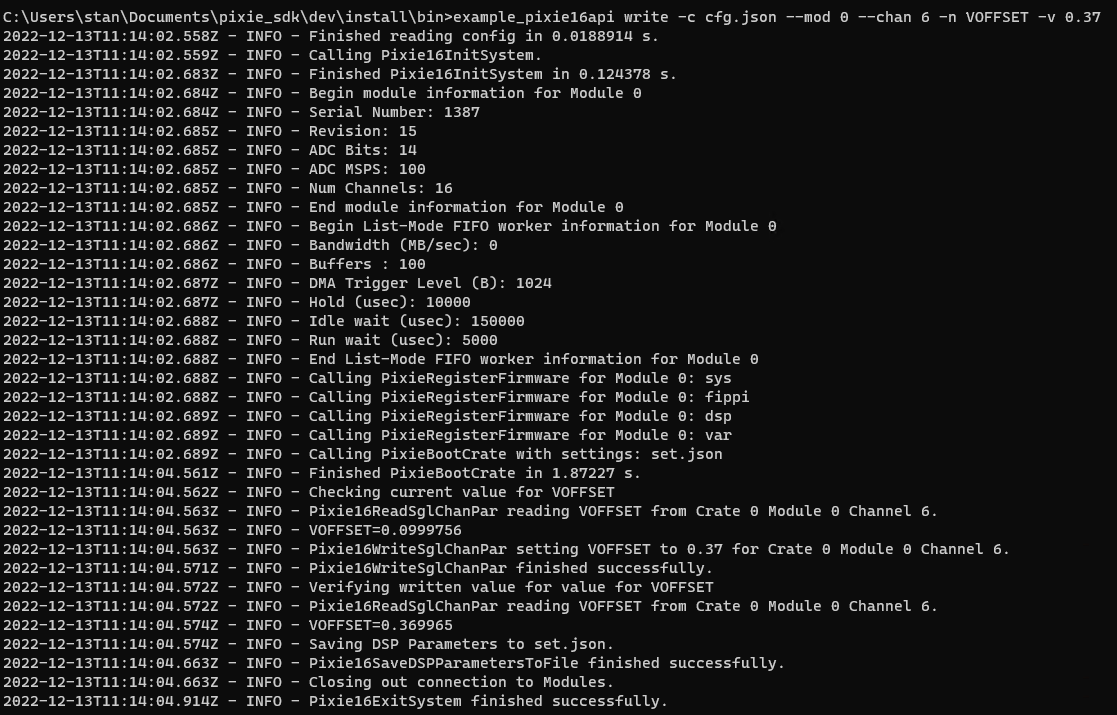
Write to all Channels in a Module#
example_pixie16api write -c cfg.json --mod 0 --chan 16 -n VOFFSET -v 0.37
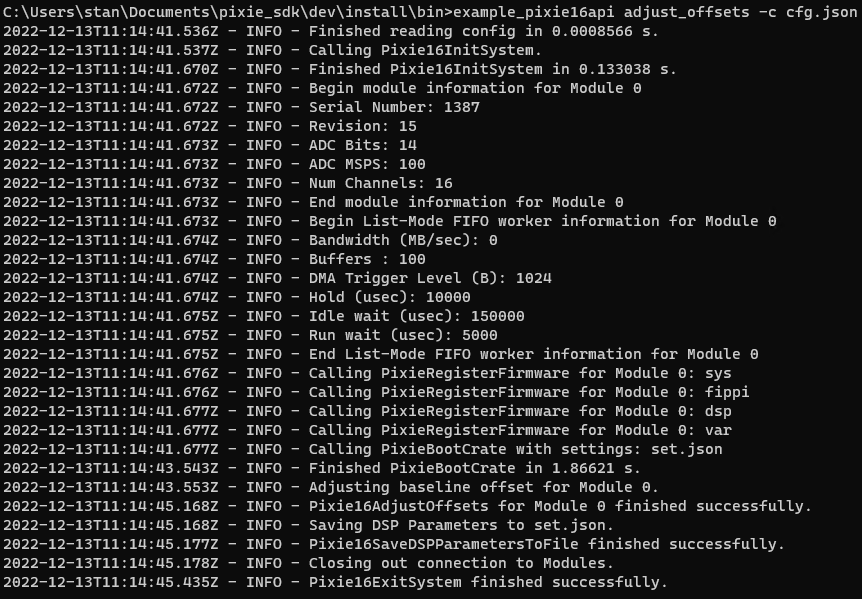
Adjust Offsets#
example_pixie16api adjust_offsets -c cfg.json --mod 0
ADC trace#
example_pixie16api trace -c cfg.json
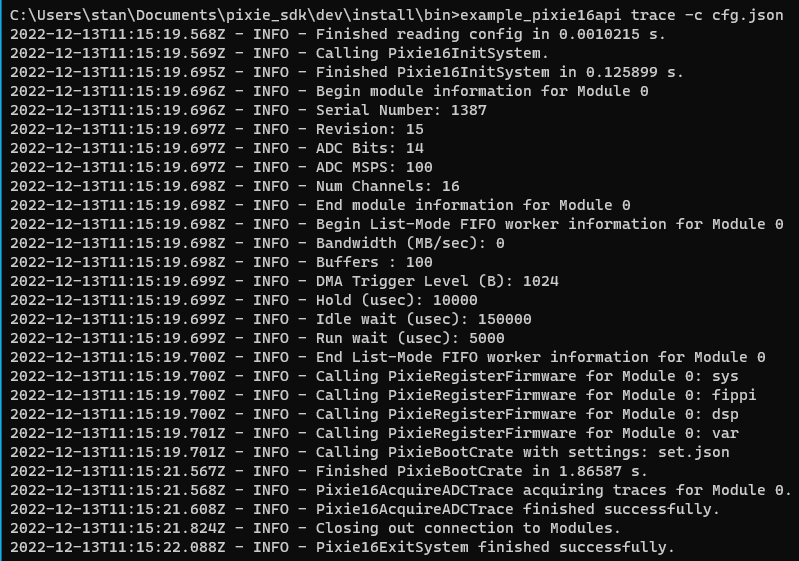
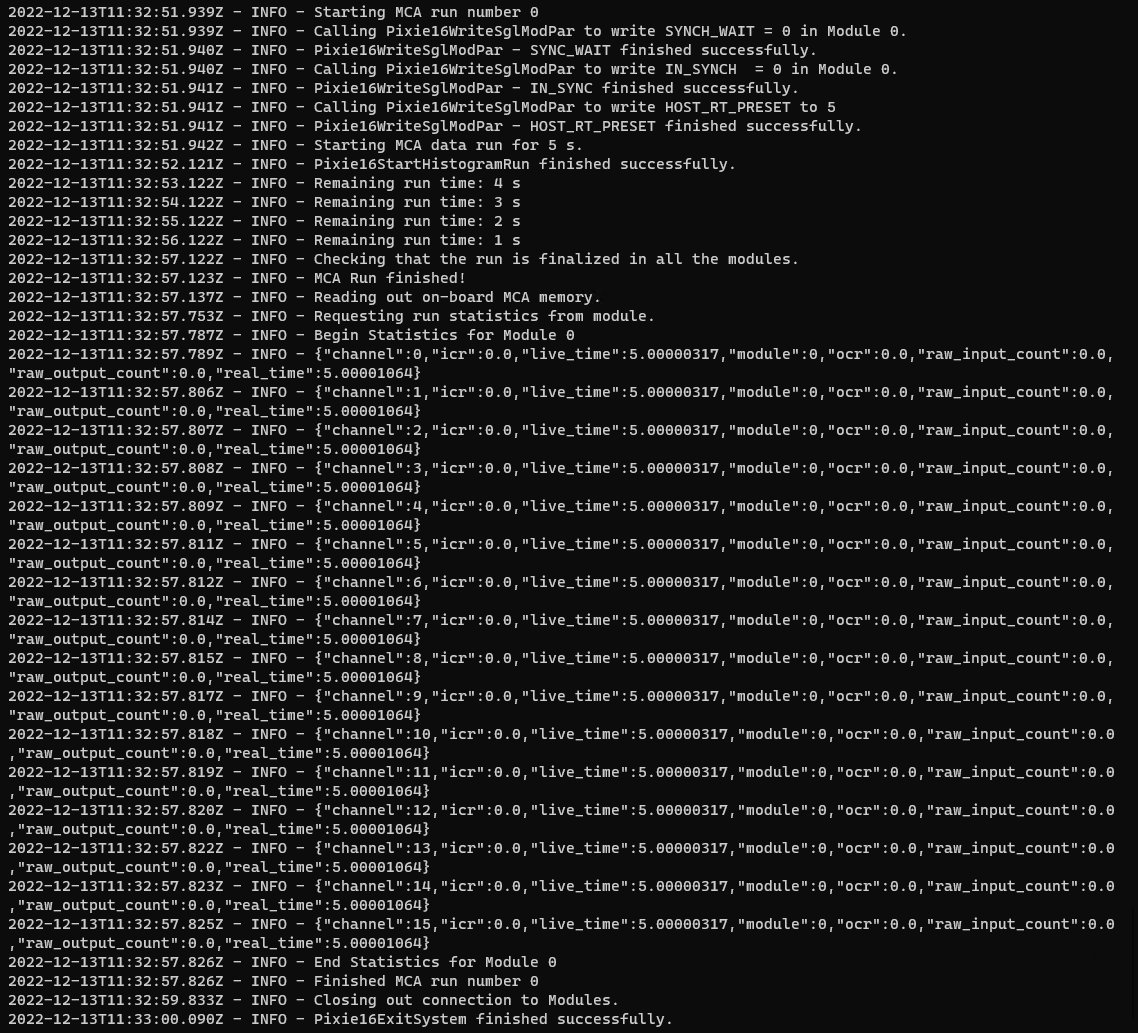
Execute a single 5 second MCA run#
example_pixie16api mca -c cfg.json -t 5
Execute 5 10 second MCA runs#
Note
When omitting the -t argument the program defaults to 10 second runs.
example_pixie16api mca -c cfg.json --num-runs 5
Execute a single 3 second list-mode run#
Note
We do not provide a screen shot of this command as it prints FIFO information to the terminal.
example_pixie16api list-mode -c cfg.json -t 3
Execute 10 10 second synchronous list-mode runs#
example_pixie16api list_mode -c cfg.json --num-runs=10 --synch-wait=1
Copy Module Parameters#
example_pixie16api copy -c cfg.json --module=0 --dest-module=4 --copy-mask=1
Copy Channel Parameters#
example_pixie16api copy -c cfg.json --module=0 --dest-module=4 --channel=3 --dest-channel=5 --copy-mask=64
Troubleshooting#
Note
In all cases, please review the log file Pixie16Msg.log for more detailed information about the errors.
Program not recognized#

Make sure the you’ve added the Pixie SDK installation paths to the user (or system) environment variable Path.
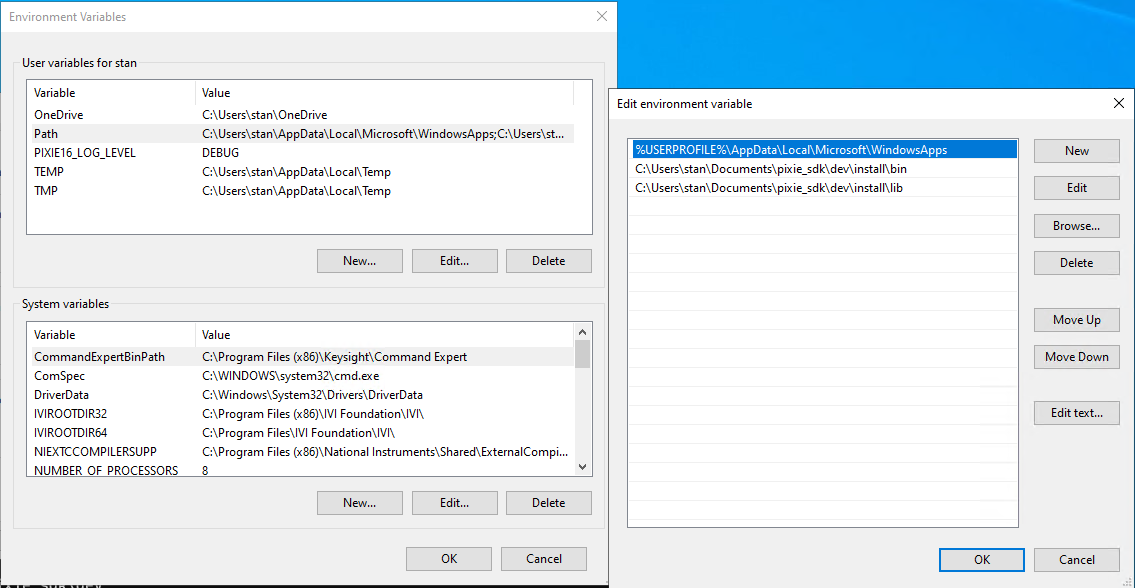
Program execution fails with “no such file”#

This is likely due to a pathing issue when providing the configuration file to the program. Please check the path is valid and that the file exists.
Boot fails with “File not Found”#

This most likely indicates an issue with the software configuration file. Please double check this file and ensure that all file paths are valid.
Reading/Writing parameter fails with “Invalid X parameter”#

This is most likely due to a mistyped parameter name. Double check the parameter name and try again. In this example, VOFFSET was mistyped as VOFFSETS.